About
Ayurveda
Ayurveda is the oldest and holistic system of medicine with its historical roots from India. The science (VEDA) that deals with the life (AYU) is called Ayurveda. Vedas consider Ayurveda as a gift of Gods to the mankind propounded from Lord “Brahma’’.
Ayurveda is considered as Upaveda (branch or sub-text) of Atharvana Veda.
Ayurveda emphasizes that health and wellness of a person depends on the balance between the mind, body, and spirit. Its main goal is to promote and preserve good health (add years to life and life to years), and to completely eradicate disease and dysfunction in the body.
Ayurveda defines Health as :-
“ SAMADOSHAHA SAMAAGNISHCHA SAMADHATU MALAKRIYAHA ।
PRASANNAATMENDRIYAMANAHA SWASTHA ITYAABHIDEEYATE ॥ ”
Health is the equilibrium state of Dosha (Bodily energies), Dhatu (Bodily tissue), proper digestion and metabolism (Agni), proper expulsion of Mala (Metabolic waste) with enthusiastic and energetic mind, body and soul. Any disturbance in equilibrium of above components leads to disease.
TRIDOSHA & PANCHA MAHABHUTA
Ayurveda believes that every person and everything in this universe is made up of five basic elements of Earth, water, fire, air & space. These combine in the human body to form three life forces/bodily humor or energies, called doshas. They control how your body works. They are Vata dosha (space and air) Pitta dosha (fire and water) & Kapha dosha (water and earth).
Everyone acquires a unique mix of the three doshas. But one dosha is usually stronger than the other. Each dosha controls a different body function. The chance of getting sick and health issues in body are developed because of the imbalance of these doshas.

Most powerful of all three doshas. It controls very basic body functions like breathing, All the movements in the body, blood flows, functions of heart, and ability to get rid of waste through your intestines,cell divisions, etc., Vata dosha also controls your mind.
This energy controls your digestion, metabolism (how well you break down foods), and certain hormones that are linked to your appetite.
This life force controls muscle growth, body strength and stability, weight, virility and immune system.
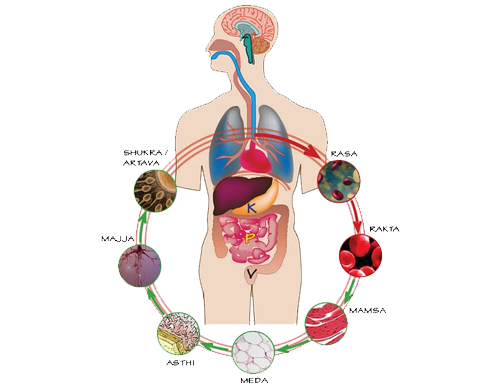
These are the seven basic tissues that make up the body and are collectively called as Sapta Dhatus. They are Rasa (Plasma), Rakta (blood), Mamsa (muscle), Medas (Fat), Asthi (bone), Majja (Bone Marrow) and Shukra (Reproductive Tissues).
These are the major excreta of the body, which are the waste products of metabolism. They are Purisha(Faeces), Mutra(Urine) and Sweda (sweat) These Tridoshas, Sapta dhatus and Trimalas (13 types in to-to) form the structural and functional components of the body. They support the body functions and contribute to the health in their own way.
HOW TO MAINTAIN HEALTH (SWASTHAVRUTTA)
As Ayurveda focuses on the safeguarding positive health, several guidelines have been mentioned in order to prevent from diseases. Some of the main practices include:
Intake of diet (Ahara) must be done as per the appetite & digestion only. Food should be taken after the digestion of previous meal digested. Food intake must not exceed 2/3rd of the capacity of the stomach. Consume light food only, Avoid Heavy diet all the times. In Ayurveda prime importance hasbeen given to Agni (Digestive fire) which plays a crucial role in the maintenance of health.
Activities done during a day decides our status of health in the future days. Hence strict guidelines have been mentioned by Acharyas like- Waking up 45 min before sunrise in the Brahma Muhurtha, Brushing the teeth using herbal twigs (Avoid bed coffee/tea before brushing), Application of collyrium to the eyes, Gargling with medicated oil (oil pulling), Body massage with oil, Physical exercise up to half of the body strength/energy only, Bathing etc.
The seasonal regimen has to be followed as per the season. This helps in controlling the imbalance of the doshas happening due to the climatic conditions and further prepares us for the challenges in upcoming season.
Due importance has been given to the voluntary and involuntary urges in Ayurveda. Involuntarily urges are Urination, Defaecation, Sneezing, Belching, Hunger, Thirst, Tears, Sleep, Vomiting etc., If these involuntary urges are withheld for longer duration, it produces systemic diseases. In the same manner Acharyas have advised to control the Voluntary urges (DHARANEEYA VEGA) like Greediness(Lobha), Grief (Shoka), Fear (Bhaya), Anger (Krodha), Ego (Ahankar), Envy (Irshya), Passion (Kama), Arrogance (Mada), Anguish (Vishada) etc.,
Three supporting pillars of body for healthy life are
1. Sleep (Nidra)
2. Food (Ahara)
3. Celibacy (Brahmacharya).
Abuse of these three leads to diseases.
By practising the above mentioned diet and regimen, one can lead a healthy life, happily.

Causes and Contributory factors for diseases

Excessive, deficit and perverted contact of sense organs with their objects. Eg: excess work in-front of computer monitors etc,.
Prajnaparada (Intellectual Blasphemy) is willfully ignoring one’s inner knowing and going against norms, intuition and common sense. It is the root cause for all diseases. Involving in verbal, mental or physical activities which are unfavourable to self harms both body and mind. Actions generated by Prajnaparada aggravate Tridosha (bodily humors) and stimulate Rajas and Tamo Gunas (psychological attributes) allowing disease to be established. Examples of prajnaparadha include any choice we make in life, whether that choice involves work or domestic life, will inevitably create an impact on our overall health and well-being. Few examples are:- • When one has eaten enough and is full yet still eats more food because it tastes so good. • When we know that smoking is harmful to one’s health but still continues to smoke cigarettes. • Viruddha aahara – Having food which is different from it’s basic properties. Eg: Ice cream followed by tea/coffe
Effect of changing time including geographical and climatic variations. Ayurveda explains that the result of deeds (kukarma) will mature in time and when it matures, the person will be afflicted with particular diseases. This is seen in some physical disorders and mostly in all mental disorders.
MANAGEMENT IN Ayurveda
Ayurveda has multi-dimensional treatment approach
This modality of treatment involves administration of oral medicine based on constitution, season and disease condition in the form of Syrup, Churna (powder), Asava-Arista , vati (tablet), Leha (liunctus), Guggulu, Bhasma, Ghrita (ghee). Few Shamana Aushadi called as Rasa aushadi contain herbo-mineral and metalic preparation which can be compared with nanomedicine of contemporary science are more target oriented in small dosage forms.
This modality of treatment involves bio-purification of body & mind named as Panchakarma , these are five therapeutic procedures namely Vamana, Virechana, Anuvasana Niruha vasti, Nasya and Rakta mokshana. These procedures are designed to eliminate toxin from the body from its nearest route.
Rasayana (Immune booster )
The main purpose of Rasayana therapy is to impede the aging process and to delay the degenerative process in the body. Rasayana is the term given to special herbs, fruits or any other form of medication that are known to promote positive health and longevity.

Prakriti Assessment
Prakriti is the major contribution of Ayurveda and is considered as one of the important diagnostic tool. According to Ayurveda, every individual is born with his or her own basic constitution, termed Prakriti which to a great extent determines inter-individual variability in susceptibility to diseases and response to external environment, diet and drugs. This system is in contrast to contemporary medicine, where a preventive and curative regime can be adopted only after an individual suffers or shows signs of an impending illness and there are no methods to identify healthy individuals who would be differently susceptible to disease. Now an integration of Ayurveda and genomics is being done in a systematic manner which we call as Ayurgenomics, which is helping to fill the gap. Ayurveda has tried to assess the diseases at genetic level centuries ago, which scientists of today are working upon.
“Thus, a person can lead a healthy and happy life by following an Ayurvedic way of living ”.
